LDD3 学习笔记
LDD3 WEEK1
关于几种
一些 log level,感觉 ERR 还挺好用的
8 #define KERN_EMERG KERN_SOH "" /* system is unusable */
9 #define KERN_ALERT KERN_SOH "" /* action must be taken immediately */
10 #define KERN_CRIT KERN_SOH "" /* critical conditions */
11 #define KERN_ERR KERN_SOH "" /* error conditions */
12 #define KERN_WARNING KERN_SOH "" /* warning conditions */
13 #define KERN_NOTICE KERN_SOH "" /* normal but significant condition */
14 #define KERN_INFO KERN_SOH "" /* informational */
15 #define KERN_DEBUG KERN_SOH "" /* debug-level messages */
16
17 #define KERN_DEFAULT KERN_SOH "" /* the default kernel loglevel */第三章续
字符设备学习,LDD3 中的代码依然能跑,seq_file 的接口有一些改变
/home/rt/kernel/scull/scull.c:142:42: error: passing argument 4 of ‘proc_create’ from incompatible pointer type [-Werror=incompatible-pointer-types]
142 | proc_create("scullseq", 0, NULL, &scullseq_proc_ops);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| |
| struct file_operations *接口有一些变化
/*
* Create a set of file operations for our proc files.
*/
// static struct file_operations scullseq_proc_ops = {
// .owner = THIS_MODULE,
// .open = scullseq_proc_open,
// .read = seq_read,
// .llseek = seq_lseek,
// .release = seq_release
// };
static struct proc_ops scullseq_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = scullseq_proc_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek,
.proc_release = seq_release
};运行结果,proc_ops 没有 owner 了,回头再看看
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull> sudo ./scull.init start
Loading scull (loading file ./scull.ko).
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull> ls /dev/scull*
/dev/scull0 /dev/scull2 /dev/scullpipe0 /dev/scullpipe2 /dev/scullpriv /dev/sculluid
/dev/scull1 /dev/scull3 /dev/scullpipe1 /dev/scullpipe3 /dev/scullsingle /dev/scullwuid
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull> ls /proc/scull*
/proc/scullseq
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull> sudo ./scull.init stop
Unloading scull.
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull> ls /dev/scull*
fish: No matches for wildcard '/dev/scull*'. See `help wildcards-globbing`.
ls /dev/scull*
^
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull [124]> ls /proc/scull*
fish: No matches for wildcard '/proc/scull*'. See `help wildcards-globbing`.
ls /proc/scull*
^Linux 2.6 的代码,基本还能用,有点震撼的。
简单测试
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# ./scull.init start
Loading scull (loading file ./scull.ko).
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# cat /dev/scull0
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# echo 2333333 > /dev/scull0
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# dmesg
[25218.564517] scull: f_pos: 24, size: 24
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# cat /dev/scull0
2333333
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# dmesg
[25218.564517] scull: f_pos: 24, size: 24
[25336.390189] scull: f_pos: 0, size: 0
[25461.386015] scull: f_pos: 0, size: 8
[25461.386018] scull: qset: 1000, quantum: 4000, itemsize: 4000000
[25461.386020] scull: item: 0, s_pos: 0, q_pos: 0
root@rogerthat:/home/rt/kernel/scull# ./scull.init stop
Unloading scull.会发现 scull_read 会在其他时候被调用,暂时不清楚原因,回头再看看。
像注册这类的函数形而上学的了解了一下,根据一些文章学习一下比较新的内核下的字符设备驱动,比如鼠标驱动 drivers/input/mouse/logibm.c,打印机驱动 drivers/char/lp.c 。Linux VERSION = 6
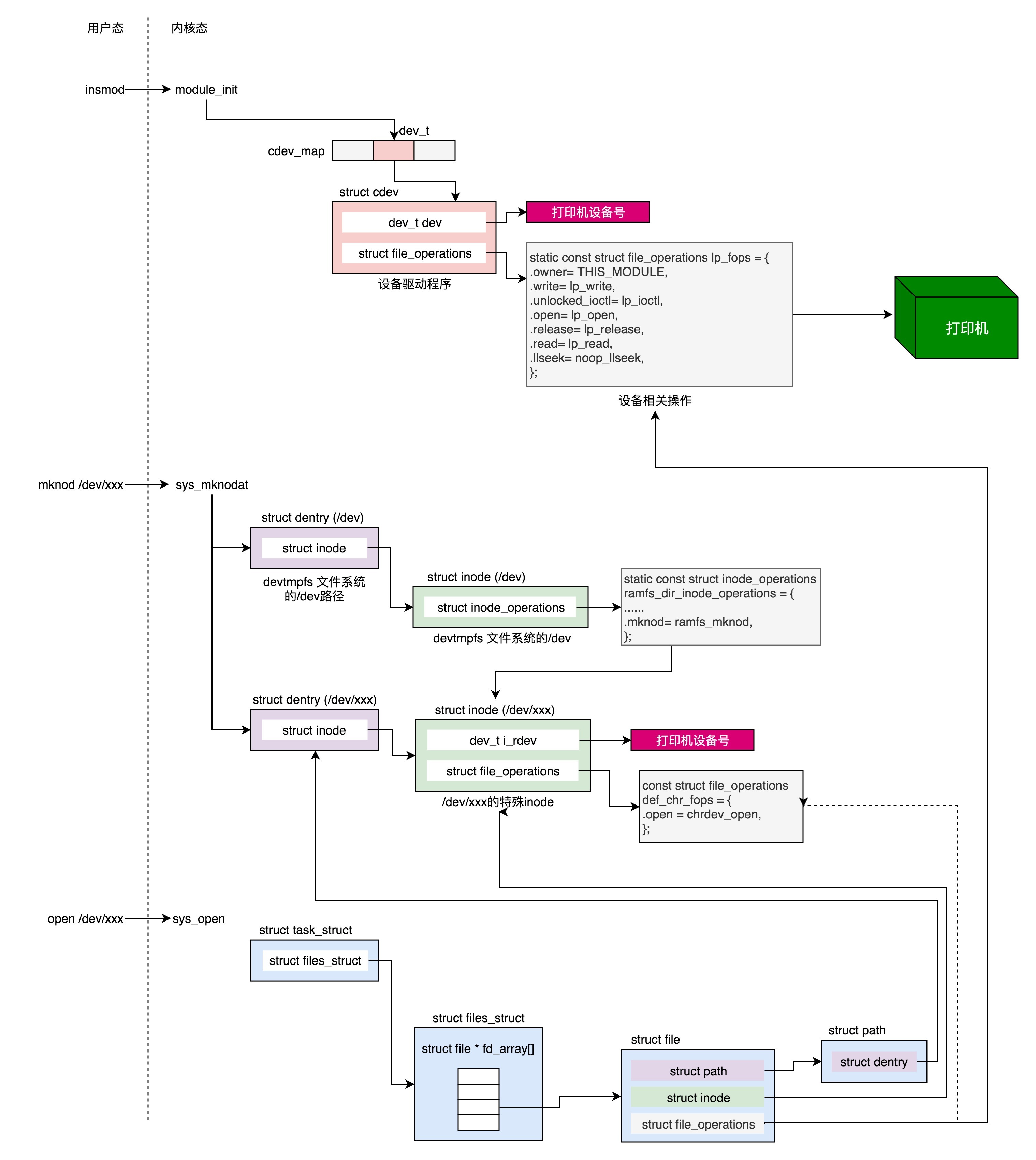
补充 struct cdev
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj; //内嵌的内核对象.
struct module *owner; //该字符设备所在的内核模块的对象指针.
const struct file_operations *ops; //该结构描述了字符设备所能实现的方法,是极为关键的一个结构体.
struct list_head list; //用来将已经向内核注册的所有字符设备形成链表.
dev_t dev; //字符设备的设备号,由主设备号和次设备号构成.
unsigned int count; //隶属于同一主设备号的次设备号的个数.
} __randomize_layout;
第四章,关于调试
ioctl TIOCLINUX
某种粗暴的方式,输出 printk 日志。
rt@rogerthat ~/k/scull [1]> sudo cat /proc/kmsg
[sudo] password for rt:
<7>[25461.386029] scull: f_pos: 8, size: 8
<7>[27016.453437] scull: f_pos: 0, size: 4
<7>[27016.453440] scull: qset: 1000, quantum: 4000, itemsize: 4000000
<7>[27016.453441] scull: item: 0, s_pos: 0, q_pos: 0printk 最终会调用到 /linux/kernel/printk/printk.c vprintk-emit c
2361 int vprintk_default(const char *fmt, va_list args)
2362 {
2363 return vprintk_emit(0, LOGLEVEL_DEFAULT, NULL, fmt, args);
2364 }
2365 EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(vprintk_default);稍微翻了一下源码,没找到环形缓存的代码,回头再看看
尝试了一下 strace 发现系统调用与以前相比,不再使用 open,而是 openat(AT_FDCWD, "/dev/scull0", O_RDONLY) = 3 ,从这个来看也没什么太大的变化。
试了一下 oops
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
*(int *)0 = 0;
return 0;
}[96688.577651] BUG: kernel NULL pointer dereference, address: 0000000000000000
[96688.577892] #PF: supervisor write access in kernel mode
[96688.577975] #PF: error_code(0x0002) - not-present page
[96688.578065] PGD 0 P4D 0
[96688.578130] Oops: 0002 [#1] PREEMPT SMP NOPTI
[96688.578242] CPU: 8 PID: 14514 Comm: bash Tainted: G OE 5.19.0-46-generic #47-Ubuntu
[96688.578354] Hardware name: QEMU Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996), BIOS rel-1.16.0-0-gd239552ce722-prebuilt.qemu.org 04/01/2014
[96688.578441] RIP: 0010:scull_write+0x9/0x1f [scull]
[96688.578522] Code: 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 5d c3 cc cc cc cc 0f 1f 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 b8 00 00 00 00 5d c3 cc cc cc cc 0f 1f 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 <c7> 04 25 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 b8 00 00 00 00 5d c3 cc cc cc cc
[96688.578679] RSP: 0018:ffffa543440d7e58 EFLAGS: 00010286
[96688.578770] RAX: ffffffffc0b870a0 RBX: 0000000000000000 RCX: ffffa543440d7ea0
[96688.578856] RDX: 0000000000000004 RSI: 0000563f3a7f4f90 RDI: ffff928fc632f800
[96688.578919] RBP: ffffa543440d7e58 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 0000000000000000
[96688.578980] R10: 0000000000000000 R11: 0000000000000000 R12: ffff928fc632f800
[96688.579045] R13: 0000000000000004 R14: ffffa543440d7ea0 R15: 0000563f3a7f4f90
[96688.579104] FS: 00007fa5a522c740(0000) GS:ffff9296dfc00000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[96688.579162] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[96688.579219] CR2: 0000000000000000 CR3: 00000001610fe000 CR4: 0000000000750ee0
[96688.579288] PKRU: 55555554
[96688.579344] Call Trace:
[96688.579396] <TASK>
[96688.579443] vfs_write+0xba/0x290
[96688.579517] ksys_write+0x73/0x100
[96688.579571] __x64_sys_write+0x19/0x30
[96688.579623] do_syscall_64+0x5b/0x90
[96688.579685] ? do_syscall_64+0x67/0x90
[96688.579738] ? syscall_exit_to_user_mode+0x29/0x50
[96688.579793] ? do_syscall_64+0x67/0x90
[96688.579847] entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+0x63/0xcd
[96688.579901] RIP: 0033:0x7fa5a510cd94
[96688.579956] Code: 15 71 90 0e 00 f7 d8 64 89 02 48 c7 c0 ff ff ff ff eb b7 0f 1f 00 f3 0f 1e fa 80 3d 4d 18 0f 00 00 74 13 b8 01 00 00 00 0f 05 <48> 3d 00 f0 ff ff 77 54 c3 0f 1f 00 48 83 ec 28 48 89 54 24 18 48
[96688.580069] RSP: 002b:00007ffd278688d8 EFLAGS: 00000202 ORIG_RAX: 0000000000000001
[96688.580126] RAX: ffffffffffffffda RBX: 0000000000000004 RCX: 00007fa5a510cd94
[96688.580185] RDX: 0000000000000004 RSI: 0000563f3a7f4f90 RDI: 0000000000000001
[96688.580240] RBP: 0000563f3a7f4f90 R08: 0000563f399f2a20 R09: 0000000000000073
[96688.580295] R10: 00000000ffffffff R11: 0000000000000202 R12: 0000000000000004
[96688.580361] R13: 00007fa5a51f7760 R14: 00007fa5a51f35e0 R15: 00007fa5a51f29e0
[96688.580446] </TASK>
[96688.580516] Modules linked in: scull(OE) tls xt_CHECKSUM ipt_REJECT nf_reject_ipv4 xt_conntrack xt_tcpudp xt_MASQUERADE nf_conntrack_netlink nft_chain_nat xfrm_user xfrm_algo nf_nat nf_conntrack xt_addrtype nf_defrag_ipv6 nft_compat nf_defrag_ipv4 br_netfilter nf_tables nfnetlink bridge stp llc intel_rapl_msr intel_rapl_common overlay cfg80211 kvm_amd ccp binfmt_misc input_leds joydev kvm serio_raw mac_hid vmgenid dm_multipath scsi_dh_rdac scsi_dh_emc scsi_dh_alua ramoops msr pstore_blk reed_solomon pstore_zone efi_pstore qemu_fw_cfg ip_tables x_tables autofs4 btrfs blake2b_generic raid10 raid456 async_raid6_recov async_memcpy async_pq async_xor async_tx xor raid6_pq libcrc32c raid1 raid0 multipath linear bochs drm_vram_helper drm_ttm_helper ttm crct10dif_pclmul drm_kms_helper syscopyarea crc32_pclmul hid_generic ghash_clmulni_intel sysfillrect sysimgblt aesni_intel usbhid virtio_net fb_sys_fops net_failover crypto_simd hid cryptd psmouse failover virtio_scsi pata_acpi drm i2c_piix4
[96688.580566] floppy [last unloaded: scull]
[96688.581822] CR2: 0000000000000000
[96688.582052] ---[ end trace 0000000000000000 ]---
[96688.582279] RIP: 0010:scull_write+0x9/0x1f [scull]
[96688.582504] Code: 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 5d c3 cc cc cc cc 0f 1f 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 b8 00 00 00 00 5d c3 cc cc cc cc 0f 1f 44 00 00 55 48 89 e5 <c7> 04 25 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 b8 00 00 00 00 5d c3 cc cc cc cc
[96688.582980] RSP: 0018:ffffa543440d7e58 EFLAGS: 00010286
[96688.583219] RAX: ffffffffc0b870a0 RBX: 0000000000000000 RCX: ffffa543440d7ea0
[96688.583458] RDX: 0000000000000004 RSI: 0000563f3a7f4f90 RDI: ffff928fc632f800
[96688.583695] RBP: ffffa543440d7e58 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 0000000000000000
[96688.583929] R10: 0000000000000000 R11: 0000000000000000 R12: ffff928fc632f800
[96688.584163] R13: 0000000000000004 R14: ffffa543440d7ea0 R15: 0000563f3a7f4f90
[96688.584385] FS: 00007fa5a522c740(0000) GS:ffff9296dfc00000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[96688.584609] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[96688.584829] CR2: 0000000000000000 CR3: 00000001610fe000 CR4: 0000000000750ee0
[96688.585051] PKRU: 55555554比较直白
第五章,并发,竞争
P,
void down(struct semaphore *sem);
int down_interruptible(struct semaphore *sem);
int down_trylock(struct semaphore *sem);V,
void up(struct semaphore *sem); 竞争很容易出 bug,比如在写锁的时候是否有考虑中断,这有可能导致死锁
三四五章的代码
scull.h
* scull.h -- definitions for the char module
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
* $Id: scull.h,v 1.15 2004/11/04 17:51:18 rubini Exp $
*/
#ifndef _SCULL_H_
#define _SCULL_H_
/*
* Macros to help debugging
*/
#undef PDEBUG /* undef it, just in case */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
# ifdef __KERNEL__
/* This one if debugging is on, and kernel space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) printk( KERN_DEBUG "scull: " fmt, ## args)
# else
/* This one for user space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) fprintf(stderr, fmt, ## args)
# endif
#else
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) /* not debugging: nothing */
#endif
#undef PDEBUGG
#define PDEBUGG(fmt, args...) /* nothing: it's a placeholder */
#ifndef SCULL_MAJOR
#define SCULL_MAJOR 0 /* dynamic major by default */
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_NR_DEVS
#define SCULL_NR_DEVS 4 /* scull0 through scull3 */
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_P_NR_DEVS
#define SCULL_P_NR_DEVS 4 /* scullpipe0 through scullpipe3 */
#endif
/*
* The bare device is a variable-length region of memory.
* Use a linked list of indirect blocks.
*
* "scull_dev->data" points to an array of pointers, each
* pointer refers to a memory area of SCULL_QUANTUM bytes.
*
* The array (quantum-set) is SCULL_QSET long.
*/
#ifndef SCULL_QUANTUM
#define SCULL_QUANTUM 4000
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_QSET
#define SCULL_QSET 1000
#endif
/*
* The pipe device is a simple circular buffer. Here its default size
*/
#ifndef SCULL_P_BUFFER
#define SCULL_P_BUFFER 4000
#endif
/*
* Representation of scull quantum sets.
*/
struct scull_qset {
void **data;
struct scull_qset *next;
};
struct scull_dev {
struct scull_qset *data; /* Pointer to first quantum set */
int quantum; /* the current quantum size */
int qset; /* the current array size */
unsigned long size; /* amount of data stored here */
struct semaphore sem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
struct cdev cdev; /* Char device structure */
};
/*
* The different configurable parameters
*/
extern int scull_major; /* main.c */
extern int scull_nr_devs;
extern int scull_quantum;
extern int scull_qset;
/*
* Prototypes for shared functions
*/
int scull_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp);
int scull_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp);
int scull_trim(struct scull_dev *dev);
ssize_t scull_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos);
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos);
loff_t scull_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t off, int whence);
#endif /* _SCULL_H_ */scull.c
包含有 /proc 的处理(使用了 seq_open 等内核函数),down_interruptible、up 同步机制。
/*
* scull.c -- the bare scull char module
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include "scull.h"
/*
* Our parameters which can be set at load time.
*/
int scull_major = SCULL_MAJOR;
int scull_minor = 0;
int scull_nr_devs = SCULL_NR_DEVS; /* number of bare scull devices */
int scull_quantum = SCULL_QUANTUM;
int scull_qset = SCULL_QSET;
module_param(scull_major, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_minor, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_nr_devs, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_quantum, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_qset, int, S_IRUGO);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Alessandro Rubini, Jonathan Corbet");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
struct scull_dev *scull_devices; /* allocated in scull_init_module */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* use proc only if debugging */
/*
* The proc filesystem: function to read and entry
*/
static void *scull_seq_start(struct seq_file *s, loff_t *pos)
{
if (*pos >= scull_nr_devs)
return NULL; /* No more to read */
return scull_devices + *pos;
}
static void *scull_seq_next(struct seq_file *s, void *v, loff_t *pos)
{
if (++(*pos) >= scull_nr_devs)
return NULL;
return scull_devices + *pos;
}
static void scull_seq_stop(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
/* Actually, there's nothing to do here */
}
static int scull_seq_show(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
struct scull_dev *dev = (struct scull_dev *) v;
struct scull_qset *d;
int i;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
seq_printf(s, "\nDevice %i: qset %i, q %i, sz %li\n", (int) (dev - scull_devices),
dev->qset, dev->quantum, dev->size);
for (d = dev->data; d; d = d->next) { /* scan the list */
seq_printf(s, " item at %p, qset at %p\n", d, d->data);
if (d->data && !d->next) { /* dump only the last item */
for (i = 0; i < dev->qset; i++) {
if (d->data[i])
seq_printf(s, " % 4i: %8p\n", i, d->data[i]);
}
}
}
up(&dev->sem);
return 0;
}
/*
* Tie the sequence operators up.
*/
static struct seq_operations scull_seq_ops = {
.start = scull_seq_start,
.next = scull_seq_next,
.stop = scull_seq_stop,
.show = scull_seq_show
};
/*
* Now to implement the /proc files we need only make an open
* method which sets up the sequence operators.
*/
static int scullseq_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return seq_open(file, &scull_seq_ops);
}
/*
* Create a set of file operations for our proc files.
*/
// static struct file_operations scullseq_proc_ops = {
// .owner = THIS_MODULE,
// .open = scullseq_proc_open,
// .read = seq_read,
// .llseek = seq_lseek,
// .release = seq_release
// };
static struct proc_ops scullseq_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = scullseq_proc_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek,
.proc_release = seq_release
};
/*
* Actually create (and remove) the /proc file(s).
*/
static void scull_create_proc(void)
{
proc_create("scullseq", 0, NULL, &scullseq_proc_ops);
}
static void scull_remove_proc(void)
{
/* no problem if it was not registered */
remove_proc_entry("scullseq", NULL);
}
#endif /* SCULL_DEBUG */
/*
* Empty out the scull device; must be called with the device
* semaphore held.
*/
int scull_trim(struct scull_dev *dev)
{
struct scull_qset *next, *dptr;
int qset = dev->qset; /* "dev" is not-null */
int i;
for (dptr = dev->data; dptr; dptr = next) { /* all the list items */
if (dptr->data) {
for (i = 0; i < qset; i++)
kfree(dptr->data[i]);
kfree(dptr->data);
dptr->data = NULL;
}
next = dptr->next;
kfree(dptr);
}
dev->size = 0;
dev->quantum = scull_quantum;
dev->qset = scull_qset;
dev->data = NULL;
return 0;
}
/*
* Open and close
*/
int scull_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct scull_dev *dev; /* device information */
dev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct scull_dev, cdev);
filp->private_data = dev; /* for other methods */
/* now trim to 0 the length of the device if open was write-only */
if ( (filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY) {
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
scull_trim(dev); /* ignore errors */
up(&dev->sem);
}
return 0; /* success */
}
int scull_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
/*
* Follow the list
*/
static struct scull_qset *scull_follow(struct scull_dev *dev, int n)
{
struct scull_qset *qs = dev->data;
/* Allocate first qset explicitly if need be */
if (! qs) {
qs = dev->data = kmalloc(sizeof(struct scull_qset), GFP_KERNEL);
if (qs == NULL)
return NULL; /* Never mind */
memset(qs, 0, sizeof(struct scull_qset));
}
/* Then follow the list */
while (n--) {
if (!qs->next) {
qs->next = kmalloc(sizeof(struct scull_qset), GFP_KERNEL);
if (qs->next == NULL)
return NULL; /* Never mind */
memset(qs->next, 0, sizeof(struct scull_qset));
}
qs = qs->next;
continue;
}
return qs;
}
/*
* Data management: read and write
*/
ssize_t scull_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr; /* the first listitem */
int quantum = dev->quantum, qset = dev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset; /* how many bytes in the listitem */
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
ssize_t retval = 0;
PDEBUG("f_pos: %lld, size: %lu", (long long) *f_pos, dev->size);
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if (*f_pos >= dev->size)
goto out;
if (*f_pos + count > dev->size)
count = dev->size - *f_pos;
/* find listitem, qset index, and offset in the quantum */
item = (long)*f_pos / itemsize;
rest = (long)*f_pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum; q_pos = rest % quantum;
PDEBUG("qset: %d, quantum: %d, itemsize: %d", qset, quantum, itemsize);
PDEBUG("item: %d, s_pos: %d, q_pos: %d", item, s_pos, q_pos);
/* follow the list up to the right position (defined elsewhere) */
dptr = scull_follow(dev, item);
if (dptr == NULL || !dptr->data || ! dptr->data[s_pos])
goto out; /* don't fill holes */
/* read only up to the end of this quantum */
if (count > quantum - q_pos)
count = quantum - q_pos;
if (copy_to_user(buf, dptr->data[s_pos] + q_pos, count)) {
retval = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
*f_pos += count;
retval = count;
out:
up(&dev->sem);
return retval;
}
// ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
// {
// *(int *)0 = 0;
// return 0;
// }
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr;
int quantum = dev->quantum, qset = dev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset;
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
ssize_t retval = -ENOMEM; /* value used in "goto out" statements */
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
/* find listitem, qset index and offset in the quantum */
item = (long)*f_pos / itemsize;
rest = (long)*f_pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum; q_pos = rest % quantum;
/* follow the list up to the right position */
dptr = scull_follow(dev, item);
if (dptr == NULL)
goto out;
if (!dptr->data) {
dptr->data = kmalloc(qset * sizeof(char *), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dptr->data)
goto out;
memset(dptr->data, 0, qset * sizeof(char *));
}
if (!dptr->data[s_pos]) {
dptr->data[s_pos] = kmalloc(quantum, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dptr->data[s_pos])
goto out;
}
/* write only up to the end of this quantum */
if (count > quantum - q_pos)
count = quantum - q_pos;
if (copy_from_user(dptr->data[s_pos]+q_pos, buf, count)) {
retval = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
*f_pos += count;
retval = count;
/* update the size */
if (dev->size < *f_pos)
dev->size = *f_pos;
out:
up(&dev->sem);
return retval;
}
/*
* The "extended" operations -- only seek
*/
loff_t scull_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t off, int whence)
{
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
loff_t newpos;
switch(whence) {
case 0: /* SEEK_SET */
newpos = off;
break;
case 1: /* SEEK_CUR */
newpos = filp->f_pos + off;
break;
case 2: /* SEEK_END */
newpos = dev->size + off;
break;
default: /* can't happen */
return -EINVAL;
}
if (newpos < 0) return -EINVAL;
filp->f_pos = newpos;
return newpos;
}
static const struct file_operations scull_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.open = scull_open,
.release = scull_release,
};
/*
* Finally, the module stuff
*/
/*
* The cleanup function is used to handle initialization failures as well.
* Thefore, it must be careful to work correctly even if some of the items
* have not been initialized
*/
void scull_cleanup_module(void)
{
int i;
dev_t devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
/* Get rid of our char dev entries */
if (scull_devices) {
for (i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++) {
scull_trim(scull_devices + i);
cdev_del(&scull_devices[i].cdev);
}
kfree(scull_devices);
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* use proc only if debugging */
scull_remove_proc();
#endif
/* cleanup_module is never called if registering failed */
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, scull_nr_devs);
}
/*
* Set up the char_dev structure for this device.
*/
static void scull_setup_cdev(struct scull_dev *dev, int index)
{
int err, devno;
devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor + index);
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &scull_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
/* Fail gracefully if need be */
if (err)
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding scull%d", err, index);
}
int scull_init_module(void)
{
int result, i;
dev_t dev = 0;
/*
* Get a range of minor numbers to work with, asking for a dynamic
* major unless directed otherwise at load time.
*/
if (scull_major) {
dev = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
result = register_chrdev_region(dev, scull_nr_devs, "scull");
} else {
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, scull_minor, scull_nr_devs, "scull");
scull_major = MAJOR(dev);
}
if (result < 0) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "scull: can't get major %d\n", scull_major);
return result;
}
/*
* allocate the devices -- we can't have them static, as the number
* can be specified at load time
*/
scull_devices = kmalloc(scull_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!scull_devices) {
result = -ENOMEM;
goto fail; /* Make this more graceful */
}
memset(scull_devices, 0, scull_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_dev));
/* Initialize each device. */
for (i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++) {
scull_devices[i].quantum = scull_quantum;
scull_devices[i].qset = scull_qset;
sema_init(&scull_devices[i].sem, 1);
scull_setup_cdev(&scull_devices[i], i);
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* only when debugging */
scull_create_proc();
#endif
return 0; /* succeed */
fail:
scull_cleanup_module();
return result;
}
module_init(scull_init_module);
module_exit(scull_cleanup_module);第六章 高级字符驱动
ioctl 内核的定义与书中的略有差别,第一个参数一般是设备,比如 usb 串口的 ioctl 第一个参数是 struct tty_struct *tty,net 的第一个参数是 struct socket *socket
ioctl 命令代码,高八位关联设备 magic number,低八位是一个顺序号(设备内唯一)
考察 /linux/include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h
现在的 ioctl-number 文档似乎在 /linux/Documentation/userspace-api/ioctl/ioctl-number.rst
对于 put_user(datum, ptr) 和 get_user(datum, ptr),我总觉得有点不好理解,实际上这个命名还是有点歧义的,感觉很有可能会有人用错。真正的命名应该是 put_to_user 和 get_from_user。如果有人理解为 put_from_user 那就完了。
一些 task 状态,/linux/include/linux/sched.h
95 #define TASK_RUNNING 0x00000000
96 #define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 0x00000001
97 #define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 0x00000002
98 #define __TASK_STOPPED 0x00000004
99 #define __TASK_TRACED 0x00000008
100 /* Used in tsk->exit_state: */
101 #define EXIT_DEAD 0x00000010
102 #define EXIT_ZOMBIE 0x00000020
103 #define EXIT_TRACE (EXIT_ZOMBIE | EXIT_DEAD)
104 /* Used in tsk->__state again: */
105 #define TASK_PARKED 0x00000040
106 #define TASK_DEAD 0x00000080
107 #define TASK_WAKEKILL 0x00000100
108 #define TASK_WAKING 0x00000200
109 #define TASK_NOLOAD 0x00000400
110 #define TASK_NEW 0x00000800
111 #define TASK_RTLOCK_WAIT 0x00001000
112 #define TASK_FREEZABLE 0x00002000
113 #define __TASK_FREEZABLE_UNSAFE (0x00004000 * IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LOCKDEP))
114 #define TASK_FROZEN 0x00008000
115 #define TASK_STATE_MAX 0x00010000
116
117 #define TASK_ANY (TASK_STATE_MAX-1)
118
119 /*
120 * DO NOT ADD ANY NEW USERS !
121 */
122 #define TASK_FREEZABLE_UNSAFE (TASK_FREEZABLE | __TASK_FREEZABLE_UNSAFE)
123
124 /* Convenience macros for the sake of set_current_state: */
125 #define TASK_KILLABLE (TASK_WAKEKILL | TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE)
126 #define TASK_STOPPED (TASK_WAKEKILL | __TASK_STOPPED)
127 #define TASK_TRACED __TASK_TRACED
128
129 #define TASK_IDLE (TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE | TASK_NOLOAD)
130
131 /* Convenience macros for the sake of wake_up(): */
132 #define TASK_NORMAL (TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE | TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE)
133
134 /* get_task_state(): */
135 #define TASK_REPORT (TASK_RUNNING | TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE | \
136 TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE | __TASK_STOPPED | \
137 __TASK_TRACED | EXIT_DEAD | EXIT_ZOMBIE | \
138 TASK_PARKED)发现看电子 pdf 效率太慢,去打印了点,笔记也在纸质上,到时候摘一点回来。
ioctl/pipe defination
存在一些兼容性问题
access_ok 第一个参数被移除
Kernel 5.0 removed VERIFY_READ and VERIFY_WRITE and removed the first
* parameter of access_ok() which was set to VERIFY_READ or VERIFY_WRITE.
* That has been redundant since kernel 2.5.70, and even then it was only
* checked for kernels that support old 386 processors.semaphore 接口改变
init_MUTEX{_LOCKED}() was initially implemented as a semaphore. Semaphores were only in older 2.6.16 kernels, now mutex replace with earlier semaphores implementation, check the below api's and linux/mutex.h headerSPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED 定义的接口改变了,现在应该使用
DEFINE_SPINLOCK(x)
源代码中的定义:
43 #define DEFINE_SPINLOCK(x) spinlock_t x = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(x)源代码对应的定义应该改为
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(scull_u_lock);
内核中对 uid_t 使用了 kuid_t 进行定义,包裹上了一个结构体,进行比较的时候不能直接使用 != 或者 = 应该使用 uid_eq(uid0, uid1)
源码中的定义:
static inline bool uid_eq(kuid_t left, kuid_t right)
54 {
55 return __kuid_val(left) == __kuid_val(right);
56 }第六章代码
scull.h
/*
* scull.h -- definitions for the char module
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
* $Id: scull.h,v 1.15 2004/11/04 17:51:18 rubini Exp $
*/
#ifndef _SCULL_H_
#define _SCULL_H_
#include <linux/ioctl.h> /* needed for the _IOW etc stuff used later */
/*
* Macros to help debugging
*/
#undef PDEBUG /* undef it, just in case */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
# ifdef __KERNEL__
/* This one if debugging is on, and kernel space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) printk( KERN_DEBUG "scull: " fmt, ## args)
# else
/* This one for user space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) fprintf(stderr, fmt, ## args)
# endif
#else
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) /* not debugging: nothing */
#endif
#undef PDEBUGG
#define PDEBUGG(fmt, args...) /* nothing: it's a placeholder */
#ifndef SCULL_MAJOR
#define SCULL_MAJOR 0 /* dynamic major by default */
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_NR_DEVS
#define SCULL_NR_DEVS 4 /* scull0 through scull3 */
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_P_NR_DEVS
#define SCULL_P_NR_DEVS 4 /* scullpipe0 through scullpipe3 */
#endif
/*
* The bare device is a variable-length region of memory.
* Use a linked list of indirect blocks.
*
* "scull_dev->data" points to an array of pointers, each
* pointer refers to a memory area of SCULL_QUANTUM bytes.
*
* The array (quantum-set) is SCULL_QSET long.
*/
#ifndef SCULL_QUANTUM
#define SCULL_QUANTUM 4000
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_QSET
#define SCULL_QSET 1000
#endif
/*
* The pipe device is a simple circular buffer. Here its default size
*/
#ifndef SCULL_P_BUFFER
#define SCULL_P_BUFFER 4000
#endif
/*
* Representation of scull quantum sets.
*/
struct scull_qset {
void **data;
struct scull_qset *next;
};
struct scull_dev {
struct scull_qset *data; /* Pointer to first quantum set */
int quantum; /* the current quantum size */
int qset; /* the current array size */
unsigned long size; /* amount of data stored here */
unsigned int access_key; /* used by sculluid and scullpriv */
struct semaphore sem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
struct cdev cdev; /* Char device structure */
};
/*
* Split minors in two parts
*/
#define TYPE(minor) (((minor) >> 4) & 0xf) /* high nibble */
#define NUM(minor) ((minor) & 0xf) /* low nibble */
/*
* The different configurable parameters
*/
extern int scull_major; /* main.c */
extern int scull_nr_devs;
extern int scull_quantum;
extern int scull_qset;
extern int scull_p_buffer; /* pipe.c */
/*
* Prototypes for shared functions
*/
int scull_p_init(dev_t dev);
void scull_p_cleanup(void);
int scull_access_init(dev_t dev);
void scull_access_cleanup(void);
int scull_trim(struct scull_dev *dev);
ssize_t scull_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos);
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos);
loff_t scull_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t off, int whence);
long scull_ioctl(struct file *filp,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
/*
* Ioctl definitions
*/
/* Use 'k' as magic number */
#define SCULL_IOC_MAGIC 'k'
/* Please use a different 8-bit number in your code */
#define SCULL_IOCRESET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 0)
/*
* S means "Set" through a ptr,
* T means "Tell" directly with the argument value
* G means "Get": reply by setting through a pointer
* Q means "Query": response is on the return value
* X means "eXchange": switch G and S atomically
* H means "sHift": switch T and Q atomically
*/
#define SCULL_IOCSQUANTUM _IOW(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 1, int)
#define SCULL_IOCSQSET _IOW(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 2, int)
#define SCULL_IOCTQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 3)
#define SCULL_IOCTQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 4)
#define SCULL_IOCGQUANTUM _IOR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 5, int)
#define SCULL_IOCGQSET _IOR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 6, int)
#define SCULL_IOCQQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 7)
#define SCULL_IOCQQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 8)
#define SCULL_IOCXQUANTUM _IOWR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 9, int)
#define SCULL_IOCXQSET _IOWR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC,10, int)
#define SCULL_IOCHQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 11)
#define SCULL_IOCHQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 12)
/*
* The other entities only have "Tell" and "Query", because they're
* not printed in the book, and there's no need to have all six.
* (The previous stuff was only there to show different ways to do it.
*/
#define SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 13)
#define SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 14)
/* ... more to come */
#define SCULL_IOC_MAXNR 14
#endif /* _SCULL_H_ */main.c
/*
* main.c -- the bare scull char module
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/errno.h> /* error codes */
#include <linux/fcntl.h> /* O_ACCMODE */
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything... */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> /* kmalloc() */
#include <linux/types.h> /* size_t */
// #include <asm/system.h> /* cli(), *_flags */
#include <asm/uaccess.h> /* copy_*_user */
#include "scull.h" /* local definitions */
/*
* Our parameters which can be set at load time.
*/
int scull_major = SCULL_MAJOR;
int scull_minor = 0;
int scull_nr_devs = SCULL_NR_DEVS; /* number of bare scull devices */
int scull_quantum = SCULL_QUANTUM;
int scull_qset = SCULL_QSET;
module_param(scull_major, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_minor, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_nr_devs, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_quantum, int, S_IRUGO);
module_param(scull_qset, int, S_IRUGO);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Alessandro Rubini, Jonathan Corbet");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
struct scull_dev *scull_devices; /* allocated in scull_init_module */
/*
* Empty out the scull device; must be called with the device
* semaphore held.
*/
int scull_trim(struct scull_dev *dev) {
struct scull_qset *next, *dptr;
int qset = dev->qset; /* "dev" is not-null */
int i;
for (dptr = dev->data; dptr; dptr = next) { /* all the list items */
if (dptr->data) {
for (i = 0; i < qset; i++)
kfree(dptr->data[i]);
kfree(dptr->data);
dptr->data = NULL;
}
next = dptr->next;
kfree(dptr);
}
dev->size = 0;
dev->quantum = scull_quantum;
dev->qset = scull_qset;
dev->data = NULL;
return 0;
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* use proc only if debugging */
/*
* The proc filesystem: function to read and entry
*/
int scull_read_procmem(char *buf, char **start, off_t offset, int count,
int *eof, void *data) {
int i, j, len = 0;
int limit = count - 80; /* Don't print more than this */
for (i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs && len <= limit; i++) {
struct scull_dev *d = &scull_devices[i];
struct scull_qset *qs = d->data;
if (down_interruptible(&d->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
len += sprintf(buf + len, "\nDevice %i: qset %i, q %i, sz %li\n", i,
d->qset, d->quantum, d->size);
for (; qs && len <= limit; qs = qs->next) { /* scan the list */
len += sprintf(buf + len, " item at %p, qset at %p\n", qs, qs->data);
if (qs->data && !qs->next) /* dump only the last item */
for (j = 0; j < d->qset; j++) {
if (qs->data[j])
len += sprintf(buf + len, " % 4i: %8p\n", j, qs->data[j]);
}
}
up(&scull_devices[i].sem);
}
*eof = 1;
return len;
}
/*
* For now, the seq_file implementation will exist in parallel. The
* older read_procmem function should maybe go away, though.
*/
/*
* Here are our sequence iteration methods. Our "position" is
* simply the device number.
*/
static void *scull_seq_start(struct seq_file *s, loff_t *pos) {
if (*pos >= scull_nr_devs)
return NULL; /* No more to read */
return scull_devices + *pos;
}
static void *scull_seq_next(struct seq_file *s, void *v, loff_t *pos) {
(*pos)++;
if (*pos >= scull_nr_devs)
return NULL;
return scull_devices + *pos;
}
static void scull_seq_stop(struct seq_file *s, void *v) {
/* Actually, there's nothing to do here */
}
static int scull_seq_show(struct seq_file *s, void *v) {
struct scull_dev *dev = (struct scull_dev *)v;
struct scull_qset *d;
int i;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
seq_printf(s, "\nDevice %i: qset %i, q %i, sz %li\n",
(int)(dev - scull_devices), dev->qset, dev->quantum, dev->size);
for (d = dev->data; d; d = d->next) { /* scan the list */
seq_printf(s, " item at %p, qset at %p\n", d, d->data);
if (d->data && !d->next) /* dump only the last item */
for (i = 0; i < dev->qset; i++) {
if (d->data[i])
seq_printf(s, " % 4i: %8p\n", i, d->data[i]);
}
}
up(&dev->sem);
return 0;
}
/*
* Tie the sequence operators up.
*/
static struct seq_operations scull_seq_ops = {.start = scull_seq_start,
.next = scull_seq_next,
.stop = scull_seq_stop,
.show = scull_seq_show};
/*
* Now to implement the /proc file we need only make an open
* method which sets up the sequence operators.
*/
static int scull_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
return seq_open(file, &scull_seq_ops);
}
/*
* Create a set of file operations for our proc file.
*/
static struct file_operations scull_proc_ops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = scull_proc_open,
.read = seq_read,
.llseek = seq_lseek,
.release = seq_release};
/*
* Actually create (and remove) the /proc file(s).
*/
static void scull_create_proc(void) {
struct proc_dir_entry *entry;
create_proc_read_entry("scullmem", 0 /* default mode */,
NULL /* parent dir */, scull_read_procmem,
NULL /* client data */);
entry = create_proc_entry("scullseq", 0, NULL);
if (entry)
entry->proc_fops = &scull_proc_ops;
}
static void scull_remove_proc(void) {
/* no problem if it was not registered */
remove_proc_entry("scullmem", NULL /* parent dir */);
remove_proc_entry("scullseq", NULL);
}
#endif /* SCULL_DEBUG */
/*
* Open and close
*/
int scull_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_dev *dev; /* device information */
dev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct scull_dev, cdev);
filp->private_data = dev; /* for other methods */
/* now trim to 0 the length of the device if open was write-only */
if ((filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY) {
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
scull_trim(dev); /* ignore errors */
up(&dev->sem);
}
return 0; /* success */
}
int scull_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { return 0; }
/*
* Follow the list
*/
struct scull_qset *scull_follow(struct scull_dev *dev, int n) {
struct scull_qset *qs = dev->data;
/* Allocate first qset explicitly if need be */
if (!qs) {
qs = dev->data = kmalloc(sizeof(struct scull_qset), GFP_KERNEL);
if (qs == NULL)
return NULL; /* Never mind */
memset(qs, 0, sizeof(struct scull_qset));
}
/* Then follow the list */
while (n--) {
if (!qs->next) {
qs->next = kmalloc(sizeof(struct scull_qset), GFP_KERNEL);
if (qs->next == NULL)
return NULL; /* Never mind */
memset(qs->next, 0, sizeof(struct scull_qset));
}
qs = qs->next;
continue;
}
return qs;
}
/*
* Data management: read and write
*/
ssize_t scull_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos) {
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr; /* the first listitem */
int quantum = dev->quantum, qset = dev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset; /* how many bytes in the listitem */
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
ssize_t retval = 0;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if (*f_pos >= dev->size)
goto out;
if (*f_pos + count > dev->size)
count = dev->size - *f_pos;
/* find listitem, qset index, and offset in the quantum */
item = (long)*f_pos / itemsize;
rest = (long)*f_pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum;
q_pos = rest % quantum;
/* follow the list up to the right position (defined elsewhere) */
dptr = scull_follow(dev, item);
if (dptr == NULL || !dptr->data || !dptr->data[s_pos])
goto out; /* don't fill holes */
/* read only up to the end of this quantum */
if (count > quantum - q_pos)
count = quantum - q_pos;
if (copy_to_user(buf, dptr->data[s_pos] + q_pos, count)) {
retval = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
*f_pos += count;
retval = count;
out:
up(&dev->sem);
return retval;
}
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos) {
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
struct scull_qset *dptr;
int quantum = dev->quantum, qset = dev->qset;
int itemsize = quantum * qset;
int item, s_pos, q_pos, rest;
ssize_t retval = -ENOMEM; /* value used in "goto out" statements */
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
/* find listitem, qset index and offset in the quantum */
item = (long)*f_pos / itemsize;
rest = (long)*f_pos % itemsize;
s_pos = rest / quantum;
q_pos = rest % quantum;
/* follow the list up to the right position */
dptr = scull_follow(dev, item);
if (dptr == NULL)
goto out;
if (!dptr->data) {
dptr->data = kmalloc(qset * sizeof(char *), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dptr->data)
goto out;
memset(dptr->data, 0, qset * sizeof(char *));
}
if (!dptr->data[s_pos]) {
dptr->data[s_pos] = kmalloc(quantum, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dptr->data[s_pos])
goto out;
}
/* write only up to the end of this quantum */
if (count > quantum - q_pos)
count = quantum - q_pos;
if (copy_from_user(dptr->data[s_pos] + q_pos, buf, count)) {
retval = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
*f_pos += count;
retval = count;
/* update the size */
if (dev->size < *f_pos)
dev->size = *f_pos;
out:
up(&dev->sem);
return retval;
}
/*
* The ioctl() implementation
*/
long scull_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) {
int err = 0, tmp;
int retval = 0;
/*
* extract the type and number bitfields, and don't decode
* wrong cmds: return ENOTTY (inappropriate ioctl) before access_ok()
*/
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != SCULL_IOC_MAGIC)
return -ENOTTY;
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) > SCULL_IOC_MAXNR)
return -ENOTTY;
/*
* the direction is a bitmask, and VERIFY_WRITE catches R/W
* transfers. `Type' is user-oriented, while
* access_ok is kernel-oriented, so the concept of "read" and
* "write" is reversed
*/
if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_READ)
err = !access_ok((void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));
else if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_WRITE)
err = !access_ok((void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));
if (err)
return -EFAULT;
switch (cmd) {
case SCULL_IOCRESET:
scull_quantum = SCULL_QUANTUM;
scull_qset = SCULL_QSET;
break;
case SCULL_IOCSQUANTUM: /* Set: arg points to the value */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
retval = __get_user(scull_quantum, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCTQUANTUM: /* Tell: arg is the value */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
scull_quantum = arg;
break;
case SCULL_IOCGQUANTUM: /* Get: arg is pointer to result */
retval = __put_user(scull_quantum, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCQQUANTUM: /* Query: return it (it's positive) */
return scull_quantum;
case SCULL_IOCXQUANTUM: /* eXchange: use arg as pointer */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
tmp = scull_quantum;
retval = __get_user(scull_quantum, (int __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0)
retval = __put_user(tmp, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCHQUANTUM: /* sHift: like Tell + Query */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
tmp = scull_quantum;
scull_quantum = arg;
return tmp;
case SCULL_IOCSQSET:
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
retval = __get_user(scull_qset, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCTQSET:
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
scull_qset = arg;
break;
case SCULL_IOCGQSET:
retval = __put_user(scull_qset, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCQQSET:
return scull_qset;
case SCULL_IOCXQSET:
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
tmp = scull_qset;
retval = __get_user(scull_qset, (int __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0)
retval = put_user(tmp, (int __user *)arg);
break;
case SCULL_IOCHQSET:
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
tmp = scull_qset;
scull_qset = arg;
return tmp;
/*
* The following two change the buffer size for scullpipe.
* The scullpipe device uses this same ioctl method, just to
* write less code. Actually, it's the same driver, isn't it?
*/
case SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE:
scull_p_buffer = arg;
break;
case SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE:
return scull_p_buffer;
default: /* redundant, as cmd was checked against MAXNR */
return -ENOTTY;
}
return retval;
}
/*
* The "extended" operations -- only seek
*/
loff_t scull_llseek(struct file *filp, loff_t off, int whence) {
struct scull_dev *dev = filp->private_data;
loff_t newpos;
switch (whence) {
case 0: /* SEEK_SET */
newpos = off;
break;
case 1: /* SEEK_CUR */
newpos = filp->f_pos + off;
break;
case 2: /* SEEK_END */
newpos = dev->size + off;
break;
default: /* can't happen */
return -EINVAL;
}
if (newpos < 0)
return -EINVAL;
filp->f_pos = newpos;
return newpos;
}
struct file_operations scull_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_open,
.release = scull_release,
};
/*
* Finally, the module stuff
*/
/*
* The cleanup function is used to handle initialization failures as well.
* Thefore, it must be careful to work correctly even if some of the items
* have not been initialized
*/
void scull_cleanup_module(void) {
int i;
dev_t devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
/* Get rid of our char dev entries */
if (scull_devices) {
for (i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++) {
scull_trim(scull_devices + i);
cdev_del(&scull_devices[i].cdev);
}
kfree(scull_devices);
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* use proc only if debugging */
scull_remove_proc();
#endif
/* cleanup_module is never called if registering failed */
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, scull_nr_devs);
/* and call the cleanup functions for friend devices */
scull_p_cleanup();
scull_access_cleanup();
}
/*
* Set up the char_dev structure for this device.
*/
static void scull_setup_cdev(struct scull_dev *dev, int index) {
int err, devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor + index);
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &scull_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
dev->cdev.ops = &scull_fops;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
/* Fail gracefully if need be */
if (err)
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding scull%d", err, index);
}
int scull_init_module(void) {
int result, i;
dev_t dev = 0;
/*
* Get a range of minor numbers to work with, asking for a dynamic
* major unless directed otherwise at load time.
*/
if (scull_major) {
dev = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
result = register_chrdev_region(dev, scull_nr_devs, "scull");
} else {
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, scull_minor, scull_nr_devs, "scull");
scull_major = MAJOR(dev);
}
if (result < 0) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "scull: can't get major %d\n", scull_major);
return result;
}
/*
* allocate the devices -- we can't have them static, as the number
* can be specified at load time
*/
scull_devices = kmalloc(scull_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!scull_devices) {
result = -ENOMEM;
goto fail; /* Make this more graceful */
}
memset(scull_devices, 0, scull_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_dev));
/* Initialize each device. */
for (i = 0; i < scull_nr_devs; i++) {
scull_devices[i].quantum = scull_quantum;
scull_devices[i].qset = scull_qset;
sema_init(&scull_devices[i].sem, 1);
scull_setup_cdev(&scull_devices[i], i);
}
/* At this point call the init function for any friend device */
dev = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor + scull_nr_devs);
dev += scull_p_init(dev);
dev += scull_access_init(dev);
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG /* only when debugging */
scull_create_proc();
#endif
return 0; /* succeed */
fail:
scull_cleanup_module();
return result;
}
module_init(scull_init_module);
module_exit(scull_cleanup_module);pipe.c
/*
* pipe.c -- fifo driver for scull
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/errno.h> /* error codes */
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything... */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk(), min() */
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> /* kmalloc() */
#include <linux/types.h> /* size_t */
#include "scull.h" /* local definitions */
struct scull_pipe {
wait_queue_head_t inq, outq; /* read and write queues */
char *buffer, *end; /* begin of buf, end of buf */
int buffersize; /* used in pointer arithmetic */
char *rp, *wp; /* where to read, where to write */
int nreaders, nwriters; /* number of openings for r/w */
struct fasync_struct *async_queue; /* asynchronous readers */
struct semaphore sem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
struct cdev cdev; /* Char device structure */
};
/* parameters */
static int scull_p_nr_devs = SCULL_P_NR_DEVS; /* number of pipe devices */
int scull_p_buffer = SCULL_P_BUFFER; /* buffer size */
dev_t scull_p_devno; /* Our first device number */
module_param(scull_p_nr_devs, int, 0); /* FIXME check perms */
module_param(scull_p_buffer, int, 0);
static struct scull_pipe *scull_p_devices;
static int scull_p_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode);
static int spacefree(struct scull_pipe *dev);
/*
* Open and close
*/
static int scull_p_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_pipe *dev;
dev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct scull_pipe, cdev);
filp->private_data = dev;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
if (!dev->buffer) {
/* allocate the buffer */
dev->buffer = kmalloc(scull_p_buffer, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev->buffer) {
up(&dev->sem);
return -ENOMEM;
}
}
dev->buffersize = scull_p_buffer;
dev->end = dev->buffer + dev->buffersize;
dev->rp = dev->wp = dev->buffer; /* rd and wr from the beginning */
/* use f_mode,not f_flags: it's cleaner (fs/open.c tells why) */
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_READ)
dev->nreaders++;
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE)
dev->nwriters++;
up(&dev->sem);
return nonseekable_open(inode, filp);
}
static int scull_p_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
/* remove this filp from the asynchronously notified filp's */
scull_p_fasync(-1, filp, 0);
down(&dev->sem);
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_READ)
dev->nreaders--;
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE)
dev->nwriters--;
if (dev->nreaders + dev->nwriters == 0) {
kfree(dev->buffer);
dev->buffer = NULL; /* the other fields are not checked on open */
}
up(&dev->sem);
return 0;
}
/*
* Data management: read and write
*/
static ssize_t scull_p_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *f_pos) {
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
while (dev->rp == dev->wp) { /* nothing to read */
up(&dev->sem); /* release the lock */
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
PDEBUG("\"%s\" reading: going to sleep\n", current->comm);
if (wait_event_interruptible(dev->inq, (dev->rp != dev->wp)))
return -ERESTARTSYS; /* signal: tell the fs layer to handle it */
/* otherwise loop, but first reacquire the lock */
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
/* ok, data is there, return something */
if (dev->wp > dev->rp)
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->wp - dev->rp));
else /* the write pointer has wrapped, return data up to dev->end */
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->end - dev->rp));
if (copy_to_user(buf, dev->rp, count)) {
up(&dev->sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
dev->rp += count;
if (dev->rp == dev->end)
dev->rp = dev->buffer; /* wrapped */
up(&dev->sem);
/* finally, awake any writers and return */
wake_up_interruptible(&dev->outq);
PDEBUG("\"%s\" did read %li bytes\n", current->comm, (long)count);
return count;
}
/* Wait for space for writing; caller must hold device semaphore. On
* error the semaphore will be released before returning. */
static int scull_getwritespace(struct scull_pipe *dev, struct file *filp) {
while (spacefree(dev) == 0) { /* full */
DEFINE_WAIT(wait);
up(&dev->sem);
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
PDEBUG("\"%s\" writing: going to sleep\n", current->comm);
prepare_to_wait(&dev->outq, &wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (spacefree(dev) == 0)
schedule();
finish_wait(&dev->outq, &wait);
if (signal_pending(current))
return -ERESTARTSYS; /* signal: tell the fs layer to handle it */
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
return 0;
}
/* How much space is free? */
static int spacefree(struct scull_pipe *dev) {
if (dev->rp == dev->wp)
return dev->buffersize - 1;
return ((dev->rp + dev->buffersize - dev->wp) % dev->buffersize) - 1;
}
static ssize_t scull_p_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *f_pos) {
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
int result;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
/* Make sure there's space to write */
result = scull_getwritespace(dev, filp);
if (result)
return result; /* scull_getwritespace called up(&dev->sem) */
/* ok, space is there, accept something */
count = min(count, (size_t)spacefree(dev));
if (dev->wp >= dev->rp)
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->end - dev->wp)); /* to end-of-buf */
else /* the write pointer has wrapped, fill up to rp-1 */
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->rp - dev->wp - 1));
PDEBUG("Going to accept %li bytes to %p from %p\n", (long)count, dev->wp,
buf);
if (copy_from_user(dev->wp, buf, count)) {
up(&dev->sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
dev->wp += count;
if (dev->wp == dev->end)
dev->wp = dev->buffer; /* wrapped */
up(&dev->sem);
/* finally, awake any reader */
wake_up_interruptible(&dev->inq); /* blocked in read() and select() */
/* and signal asynchronous readers, explained late in chapter 5 */
if (dev->async_queue)
kill_fasync(&dev->async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
PDEBUG("\"%s\" did write %li bytes\n", current->comm, (long)count);
return count;
}
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait) {
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem);
return mask;
}
static int scull_p_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode) {
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
return fasync_helper(fd, filp, mode, &dev->async_queue);
}
/* FIXME this should use seq_file */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
static void scullp_proc_offset(char *buf, char **start, off_t *offset,
int *len) {
if (*offset == 0)
return;
if (*offset >= *len) { /* Not there yet */
*offset -= *len;
*len = 0;
} else { /* We're into the interesting stuff now */
*start = buf + *offset;
*offset = 0;
}
}
static int scull_read_p_mem(char *buf, char **start, off_t offset, int count,
int *eof, void *data) {
int i, len;
struct scull_pipe *p;
#define LIMIT (PAGE_SIZE - 200) /* don't print any more after this size */
*start = buf;
len = sprintf(buf, "Default buffersize is %i\n", scull_p_buffer);
for (i = 0; i < scull_p_nr_devs && len <= LIMIT; i++) {
p = &scull_p_devices[i];
if (down_interruptible(&p->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
len += sprintf(buf + len, "\nDevice %i: %p\n", i, p);
/* len += sprintf(buf+len, " Queues: %p %p\n", p->inq,
* p->outq);*/
len += sprintf(buf + len, " Buffer: %p to %p (%i bytes)\n", p->buffer,
p->end, p->buffersize);
len += sprintf(buf + len, " rp %p wp %p\n", p->rp, p->wp);
len += sprintf(buf + len, " readers %i writers %i\n", p->nreaders,
p->nwriters);
up(&p->sem);
scullp_proc_offset(buf, start, &offset, &len);
}
*eof = (len <= LIMIT);
return len;
}
#endif
/*
* The file operations for the pipe device
* (some are overlayed with bare scull)
*/
struct file_operations scull_pipe_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = scull_p_read,
.write = scull_p_write,
.poll = scull_p_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_p_open,
.release = scull_p_release,
.fasync = scull_p_fasync,
};
/*
* Set up a cdev entry.
*/
static void scull_p_setup_cdev(struct scull_pipe *dev, int index) {
int err, devno = scull_p_devno + index;
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &scull_pipe_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
/* Fail gracefully if need be */
if (err)
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding scullpipe%d", err, index);
}
/*
* Initialize the pipe devs; return how many we did.
*/
int scull_p_init(dev_t firstdev) {
int i, result;
result = register_chrdev_region(firstdev, scull_p_nr_devs, "scullp");
if (result < 0) {
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Unable to get scullp region, error %d\n", result);
return 0;
}
scull_p_devno = firstdev;
scull_p_devices =
kmalloc(scull_p_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_pipe), GFP_KERNEL);
if (scull_p_devices == NULL) {
unregister_chrdev_region(firstdev, scull_p_nr_devs);
return 0;
}
memset(scull_p_devices, 0, scull_p_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_pipe));
for (i = 0; i < scull_p_nr_devs; i++) {
init_waitqueue_head(&(scull_p_devices[i].inq));
init_waitqueue_head(&(scull_p_devices[i].outq));
sema_init(&scull_p_devices[i].sem, 1);
scull_p_setup_cdev(scull_p_devices + i, i);
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
create_proc_read_entry("scullpipe", 0, NULL, scull_read_p_mem, NULL);
#endif
return scull_p_nr_devs;
}
/*
* This is called by cleanup_module or on failure.
* It is required to never fail, even if nothing was initialized first
*/
void scull_p_cleanup(void) {
int i;
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
remove_proc_entry("scullpipe", NULL);
#endif
if (!scull_p_devices)
return; /* nothing else to release */
for (i = 0; i < scull_p_nr_devs; i++) {
cdev_del(&scull_p_devices[i].cdev);
kfree(scull_p_devices[i].buffer);
}
kfree(scull_p_devices);
unregister_chrdev_region(scull_p_devno, scull_p_nr_devs);
scull_p_devices = NULL; /* pedantic */
}access.c
/*
* access.c -- the files with access control on open
*
* Copyright (C) 2001 Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet
* Copyright (C) 2001 O'Reilly & Associates
*
* The source code in this file can be freely used, adapted,
* and redistributed in source or binary form, so long as an
* acknowledgment appears in derived source files. The citation
* should list that the code comes from the book "Linux Device
* Drivers" by Alessandro Rubini and Jonathan Corbet, published
* by O'Reilly & Associates. No warranty is attached;
* we cannot take responsibility for errors or fitness for use.
*
* $Id: access.c,v 1.17 2004/09/26 07:29:56 gregkh Exp $
*/
/* FIXME: cloned devices as a use for kobjects? */
#include <asm/atomic.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/errno.h> /* error codes */
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/fs.h> /* everything... */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* printk() */
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> /* kmalloc() */
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/types.h> /* size_t */
#include "scull.h" /* local definitions */
static dev_t scull_a_firstdev; /* Where our range begins */
/*
* These devices fall back on the main scull operations. They only
* differ in the implementation of open() and close()
*/
/************************************************************************
*
* The first device is the single-open one,
* it has an hw structure and an open count
*/
static struct scull_dev scull_s_device;
static atomic_t scull_s_available = ATOMIC_INIT(1);
static int scull_s_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_dev *dev = &scull_s_device; /* device information */
if (!atomic_dec_and_test(&scull_s_available)) {
atomic_inc(&scull_s_available);
return -EBUSY; /* already open */
}
/* then, everything else is copied from the bare scull device */
if ((filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY)
scull_trim(dev);
filp->private_data = dev;
return 0; /* success */
}
static int scull_s_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
atomic_inc(&scull_s_available); /* release the device */
return 0;
}
/*
* The other operations for the single-open device come from the bare device
*/
struct file_operations scull_sngl_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_s_open,
.release = scull_s_release,
};
/************************************************************************
*
* Next, the "uid" device. It can be opened multiple times by the
* same user, but access is denied to other users if the device is open
*/
static struct scull_dev scull_u_device;
static int scull_u_count; /* initialized to 0 by default */
static kuid_t scull_u_owner; /* initialized to 0 by default */
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(scull_u_lock);
static int scull_u_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_dev *dev = &scull_u_device; /* device information */
spin_lock(&scull_u_lock);
if (scull_u_count &&
!uid_eq(scull_u_owner, current_cred()->uid) && /* allow user */
!uid_eq(scull_u_owner, current_cred()->euid) && /* allow whoever did su */
!capable(CAP_DAC_OVERRIDE)) { /* still allow root */
spin_unlock(&scull_u_lock);
return -EBUSY; /* -EPERM would confuse the user */
}
if (scull_u_count == 0)
scull_u_owner = current_cred()->uid; /* grab it */
scull_u_count++;
spin_unlock(&scull_u_lock);
/* then, everything else is copied from the bare scull device */
if ((filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY)
scull_trim(dev);
filp->private_data = dev;
return 0; /* success */
}
static int scull_u_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
spin_lock(&scull_u_lock);
scull_u_count--; /* nothing else */
spin_unlock(&scull_u_lock);
return 0;
}
/*
* The other operations for the device come from the bare device
*/
struct file_operations scull_user_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_u_open,
.release = scull_u_release,
};
/************************************************************************
*
* Next, the device with blocking-open based on uid
*/
static struct scull_dev scull_w_device;
static int scull_w_count; /* initialized to 0 by default */
static kuid_t scull_w_owner; /* initialized to 0 by default */
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(scull_w_wait);
// static spinlock_t scull_w_lock = SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED;
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(scull_w_lock);
static inline int scull_w_available(void) {
return scull_w_count == 0 || uid_eq(scull_w_owner, current_cred()->uid) ||
uid_eq(scull_w_owner, current_cred()->euid) ||
capable(CAP_DAC_OVERRIDE);
}
static int scull_w_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_dev *dev = &scull_w_device; /* device information */
spin_lock(&scull_w_lock);
while (!scull_w_available()) {
spin_unlock(&scull_w_lock);
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (wait_event_interruptible(scull_w_wait, scull_w_available()))
return -ERESTARTSYS; /* tell the fs layer to handle it */
spin_lock(&scull_w_lock);
}
if (scull_w_count == 0)
scull_w_owner = current_cred()->uid; /* grab it */
scull_w_count++;
spin_unlock(&scull_w_lock);
/* then, everything else is copied from the bare scull device */
if ((filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY)
scull_trim(dev);
filp->private_data = dev;
return 0; /* success */
}
static int scull_w_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
int temp;
spin_lock(&scull_w_lock);
scull_w_count--;
temp = scull_w_count;
spin_unlock(&scull_w_lock);
if (temp == 0)
wake_up_interruptible_sync(&scull_w_wait); /* awake other uid's */
return 0;
}
/*
* The other operations for the device come from the bare device
*/
struct file_operations scull_wusr_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_w_open,
.release = scull_w_release,
};
/************************************************************************
*
* Finally the `cloned' private device. This is trickier because it
* involves list management, and dynamic allocation.
*/
/* The clone-specific data structure includes a key field */
struct scull_listitem {
struct scull_dev device;
dev_t key;
struct list_head list;
};
/* The list of devices, and a lock to protect it */
static LIST_HEAD(scull_c_list);
// static spinlock_t scull_c_lock = SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED;
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(scull_c_lock);
/* A placeholder scull_dev which really just holds the cdev stuff. */
static struct scull_dev scull_c_device;
/* Look for a device or create one if missing */
static struct scull_dev *scull_c_lookfor_device(dev_t key) {
struct scull_listitem *lptr;
list_for_each_entry(lptr, &scull_c_list, list) {
if (lptr->key == key)
return &(lptr->device);
}
/* not found */
lptr = kmalloc(sizeof(struct scull_listitem), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!lptr)
return NULL;
/* initialize the device */
memset(lptr, 0, sizeof(struct scull_listitem));
lptr->key = key;
scull_trim(&(lptr->device)); /* initialize it */
sema_init(&(lptr->device.sem), 1);
/* place it in the list */
list_add(&lptr->list, &scull_c_list);
return &(lptr->device);
}
static int scull_c_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
struct scull_dev *dev;
dev_t key;
if (!current->signal->tty) {
PDEBUG("Process \"%s\" has no ctl tty\n", current->comm);
return -EINVAL;
}
key = tty_devnum(current->signal->tty);
/* look for a scullc device in the list */
spin_lock(&scull_c_lock);
dev = scull_c_lookfor_device(key);
spin_unlock(&scull_c_lock);
if (!dev)
return -ENOMEM;
/* then, everything else is copied from the bare scull device */
if ((filp->f_flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY)
scull_trim(dev);
filp->private_data = dev;
return 0; /* success */
}
static int scull_c_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
/*
* Nothing to do, because the device is persistent.
* A `real' cloned device should be freed on last close
*/
return 0;
}
/*
* The other operations for the device come from the bare device
*/
struct file_operations scull_priv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = scull_llseek,
.read = scull_read,
.write = scull_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = scull_ioctl,
.open = scull_c_open,
.release = scull_c_release,
};
/************************************************************************
*
* And the init and cleanup functions come last
*/
static struct scull_adev_info {
char *name;
struct scull_dev *sculldev;
struct file_operations *fops;
} scull_access_devs[] = {{"scullsingle", &scull_s_device, &scull_sngl_fops},
{"sculluid", &scull_u_device, &scull_user_fops},
{"scullwuid", &scull_w_device, &scull_wusr_fops},
{"sullpriv", &scull_c_device, &scull_priv_fops}};
#define SCULL_N_ADEVS 4
/*
* Set up a single device.
*/
static void scull_access_setup(dev_t devno, struct scull_adev_info *devinfo) {
struct scull_dev *dev = devinfo->sculldev;
int err;
/* Initialize the device structure */
dev->quantum = scull_quantum;
dev->qset = scull_qset;
sema_init(&dev->sem, 1);
/* Do the cdev stuff. */
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, devinfo->fops);
kobject_set_name(&dev->cdev.kobj, devinfo->name);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
/* Fail gracefully if need be */
if (err) {
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding %s\n", err, devinfo->name);
kobject_put(&dev->cdev.kobj);
} else
printk(KERN_NOTICE "%s registered at %x\n", devinfo->name, devno);
}
int scull_access_init(dev_t firstdev) {
int result, i;
/* Get our number space */
result = register_chrdev_region(firstdev, SCULL_N_ADEVS, "sculla");
if (result < 0) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "sculla: device number registration failed\n");
return 0;
}
scull_a_firstdev = firstdev;
/* Set up each device. */
for (i = 0; i < SCULL_N_ADEVS; i++)
scull_access_setup(firstdev + i, scull_access_devs + i);
return SCULL_N_ADEVS;
}
/*
* This is called by cleanup_module or on failure.
* It is required to never fail, even if nothing was initialized first
*/
void scull_access_cleanup(void) {
struct scull_listitem *lptr, *next;
int i;
/* Clean up the static devs */
for (i = 0; i < SCULL_N_ADEVS; i++) {
struct scull_dev *dev = scull_access_devs[i].sculldev;
cdev_del(&dev->cdev);
scull_trim(scull_access_devs[i].sculldev);
}
/* And all the cloned devices */
list_for_each_entry_safe(lptr, next, &scull_c_list, list) {
list_del(&lptr->list);
scull_trim(&(lptr->device));
kfree(lptr);
}
/* Free up our number space */
unregister_chrdev_region(scull_a_firstdev, SCULL_N_ADEVS);
return;
}第六章代码测试
关于 ioctl
我在 scull_ioctl 中插入一个 log
switch (cmd) {
case SCULL_IOCRESET:
printk(KERN_WARNING "scull ioctl cmd: SCULL_IOCRESET arg:%lu\n", arg);
scull_quantum = SCULL_QUANTUM;
scull_qset = SCULL_QSET;
break;测试代码
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define SCULL_IOC_MAGIC 'k'
#define SCULL_IOCRESET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 0)
#define SCULL_IOCSQUANTUM _IOW(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 1, int)
#define SCULL_IOCSQSET _IOW(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 2, int)
#define SCULL_IOCTQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 3)
#define SCULL_IOCTQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 4)
#define SCULL_IOCGQUANTUM _IOR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 5, int)
#define SCULL_IOCGQSET _IOR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 6, int)
#define SCULL_IOCQQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 7)
#define SCULL_IOCQQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 8)
#define SCULL_IOCXQUANTUM _IOWR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 9, int)
#define SCULL_IOCXQSET _IOWR(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC,10, int)
#define SCULL_IOCHQUANTUM _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 11)
#define SCULL_IOCHQSET _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 12)
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int arg = 114514;
int fd = open("/dev/scull0", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("fopen error number: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
if (ioctl(fd, SCULL_IOCRESET, arg) == -1) {
printf("ioctl error number: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}编译后执行,结果如下
rt@rogerthat ~/k/s/test> sudo dmesg -C
rt@rogerthat ~/k/s/test> ./a.out
rt@rogerthat ~/k/s/test> sudo dmesg
[ 5814.272212] scull ioctl cmd: SCULL_IOCRESET arg:114514关于阻塞读写
踩了坑,他分配的设备 MINOR 和 scull.init 对不上,导致找不到对应设备



关于非阻塞读写
有点问题,为啥这个 read 读不出东西,回头再看看了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int fd = open("/dev/scullpipe0", O_WRONLY | O_RDONLY | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("fopen error number: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
// nonblock read
char buf[5];
read(fd, buf, 4);
printf("Read: %s\n", buf);
// nonblock write
// write long string
char long_string[4002]; // larger than pip buffer
memset(long_string, 'a', 4001);
long_string[4001] = '\0';
write(fd, long_string, 4001);
printf("Write a long string\n");
// fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, fcntl(fd, F_GETFL) | O_NONBLOCK);
close(fd);
return 0;
}结果







